Thailand ranked the 46th place on the ease of doing business by the World Bank Group in year 2017. The government aims to bring the Kingdom to the world’s top 20 by May 2017. The government plans to upgrade the efficiency of doing business by approve a business via an electronic registration system so the setup time will be less than 20 days.
Department of Business Development, Ministry of Commerce is responsible for setup company in Thailand. Board of Investment (BOI), Prime Minister’s Office is responsible for promoting foreign and domestic investment and approving most project proposals in Thailand. With the strong support from government, foreign investor can enjoy many benefits doing business in Thailand.
Right time, right place
Thailand has a strong government support for foreign companies to invest in Thailand. BOI offers an attractive and competitive package of tax incentives. BOI has set up free zones and industrial zones with aim of build a strong cluster for the industries. Manufacturers who located in these zones will be able to enjoy benefits such as exemption for import duty for machinery, exemption of raw material import duty when products are going to be re-export.
In January 2015, a BOI “Five Special Economic Zones” was implemented to support ASEAN Economic Community. The new economic zone are:
- Mae Sot/Tak: Thailand/Myanamar border
- Sadao/Songkhla: Thailand/Malaysia border
- Mukdahan: Thailand/Lao border
- Aranyaprathet/Sa Kaeo: Thailand/Cambodia border
- Klong Yai/Trat: Thailand/Cambodia border
The opening of AEC is likely to increase manufacturing in Myanmar, Cambodia and Laos due to the cheaper labour cost. Thailand with the well established infrastructure will be able to act as a regional hub for trade, transportation, and efficient production chain in the region.
Investment project in these special economic zones will receive corporate income tax exemption for three years more than the normal criteria.
Type of legal presence in Thailand
There are various ways for an investor to enter Thailand, depending on the investor’s type of business. Types of legal presence for foreign direct investment in Thailand are:
Direct investment:
- Partnership
- Limited company
- International Headquarters (IHQ)
- Representative office
Indirect investment
- Agent / Distributor
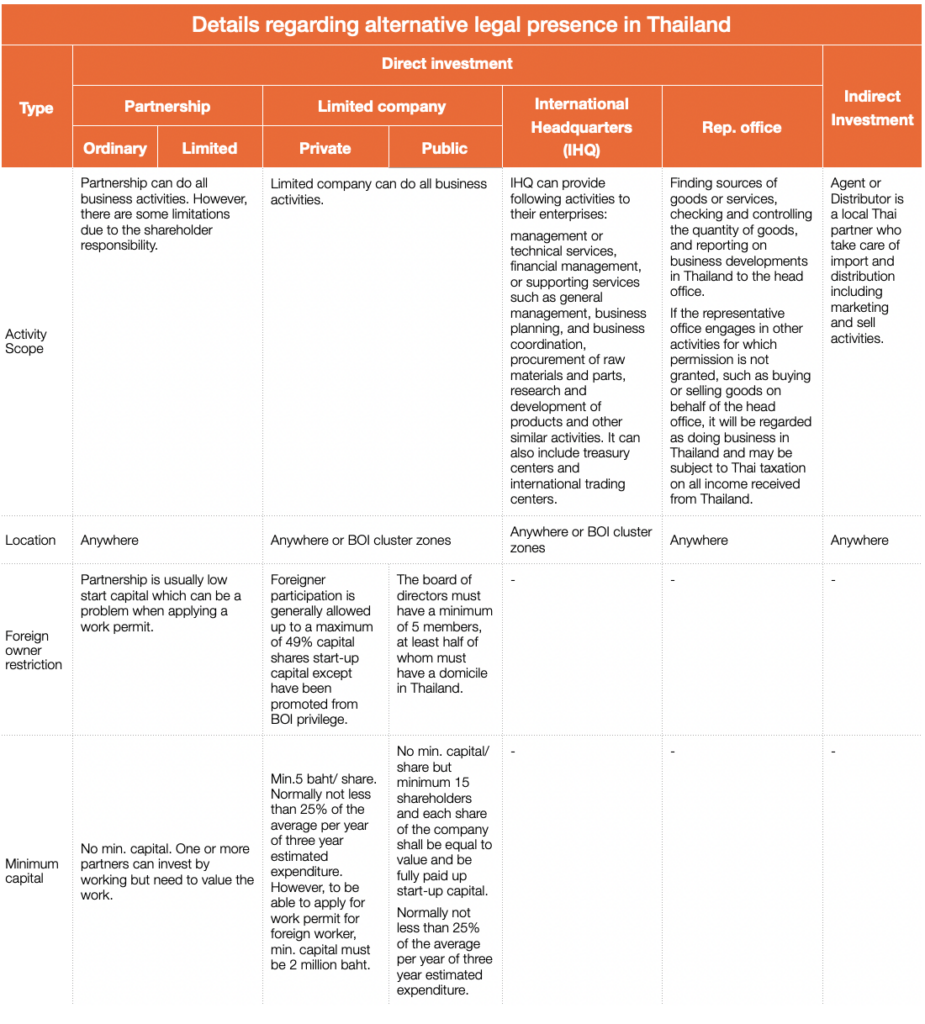
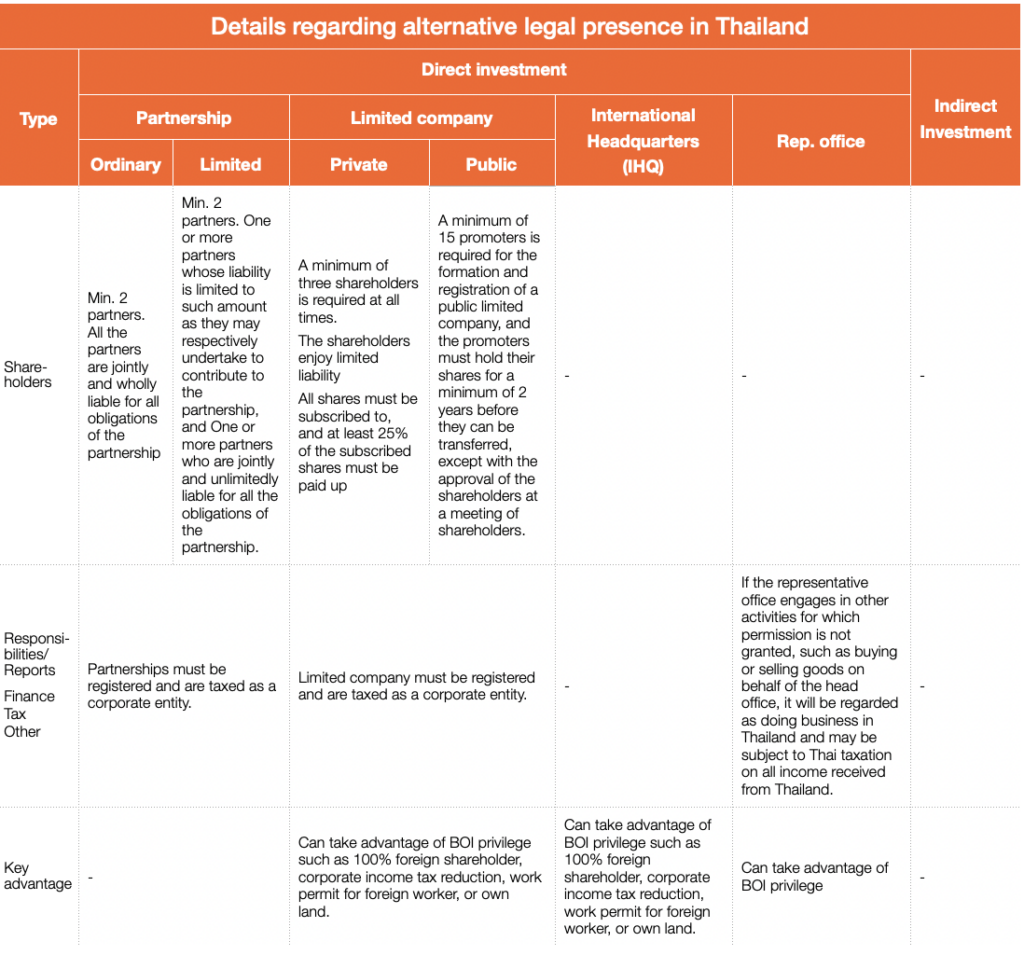
The most common way for a foreign company to enter Thailand is starting up a limited company. Limited company will allow you to hire foreigner to work in the country. (Please see list below of profession which is not allow foreigner to work.)
Restricted Occupations
A Royal Decree in 1973 listed 39 occupations and professions that were then prohibited to foreigners. This list has been amended on several occasions by subsequent Royal Decrees, the latest one in 2005:
- Labor work, except crewmen engaging in fishery activities included under Item 2 below;
- Cultivation, animal breeding, forestry and fishery work, except for labor work in maritime fisheries and work requiring specific skills in farm supervision;
- Masonry, carpentry, or other construction work;
- Wood carving;
- Driving motor vehicles or nonmotorized carriers, except for piloting international aircraft;
- Shop attendant;
- Auctioneering;
- Supervising, auditing or giving services in accounting, except occasional international auditing;
- Gem cutting and polishing;
- Hair cutting, hairdressing and beautician work;
- Hand weaving;
- Mat weaving or making of wares from reed, rattan, kenaf, straw or bamboo pulp;
- Manufacture of manual fibrous paper;
- Manufacture of lacquerware;
- Thai musical instrument production;
- Manufacture of nielloware;
- Goldsmith, silversmith and other precious metal work;
- Manufacture of bronzeware;
- Thai doll making;
- Manufacture of mattresses and padded blankets;
- Alms bowl making;
- Manual silk product making;
- Buddha image making;
- Manufacture of knives;
- Paper and cloth umbrella fabrication;
- Shoemaking;
- Hat making;
- Brokerage or agency work, except in international business;
- Engineering work, civil engineering branch, that concerns planning and calculation, systemization, research, planning, testing, construction supervision or advisory work, except work requiring specialized skills;
- Architectural work concerning designing, drawing, estimating, construction supervision, or advisory work;
- Dressmaking;
- Pottery or ceramics;
- Manual cigarette rolling;
- Tourist guide or tour organizing agency;
- Hawking business;
- Thai character type setting;
- Manual silk reeling and weaving;
- Clerical or secretarial work;
- Legal or litigation service, except: (a) Working as arbitrator (b) Conducting lawsuits in Arbitration Court in cases where the law which enforces the dispute is not Thai Law or in cases that do not require judgment of Arbitration in the Kingdom of Thailand
Limited company will be able to apply for BOI privilege and enjoy benefits from BOI such as a possibility of having 100% foreign shareholders, import and re-export duty exemption, CIT exemption and landowner. In retail business, distributor is one alternative.
Rising Stars in Southeast Asia – Business Opportunity Analysis

